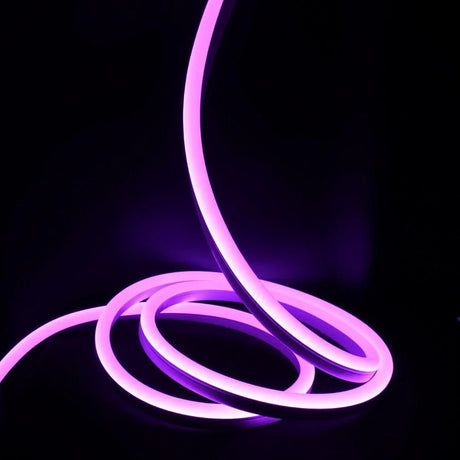
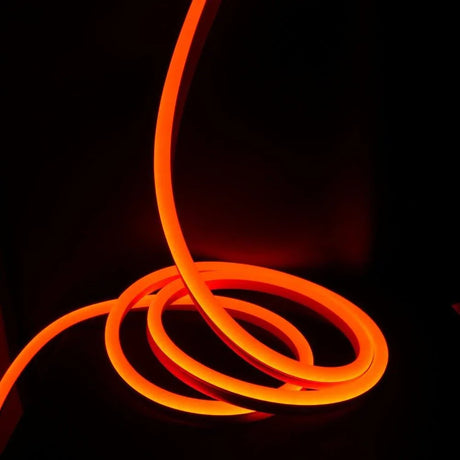
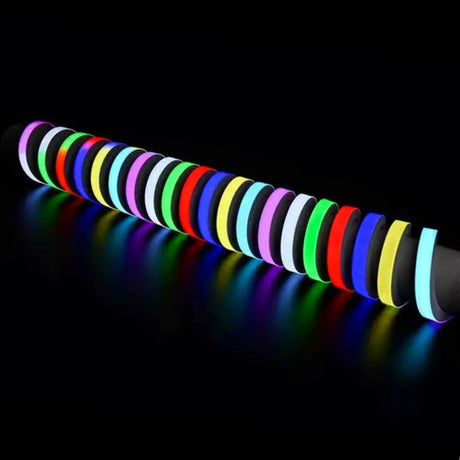
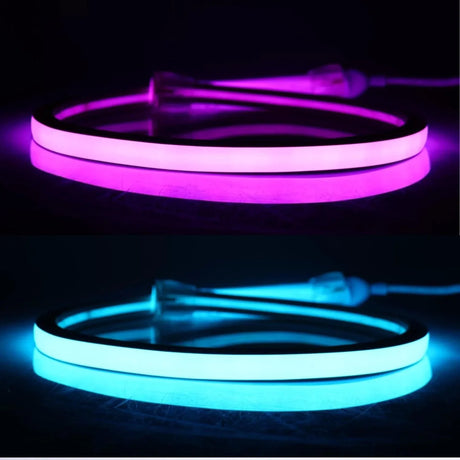
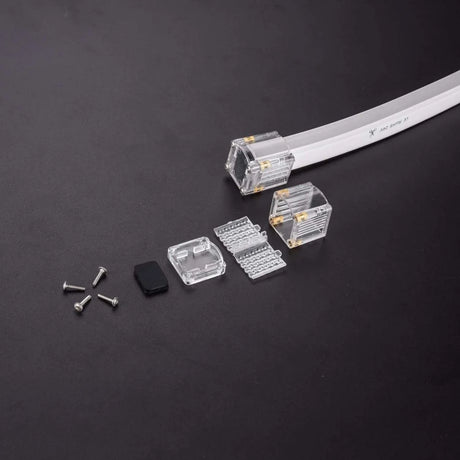
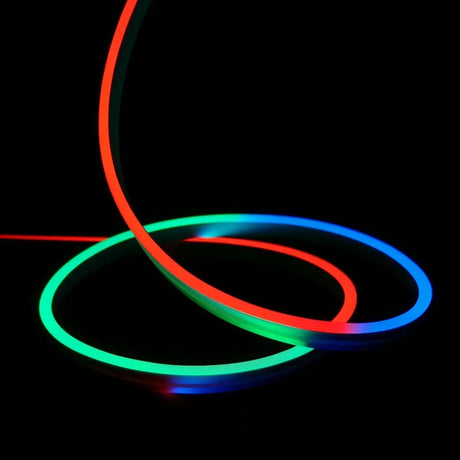
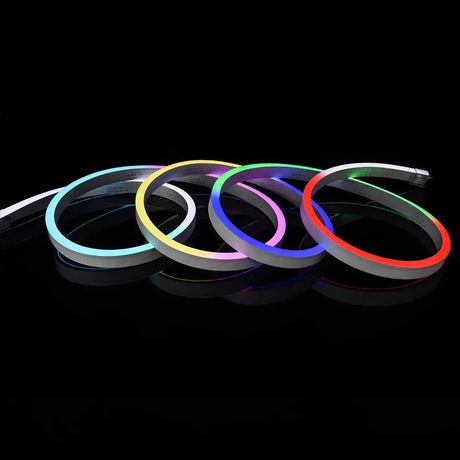
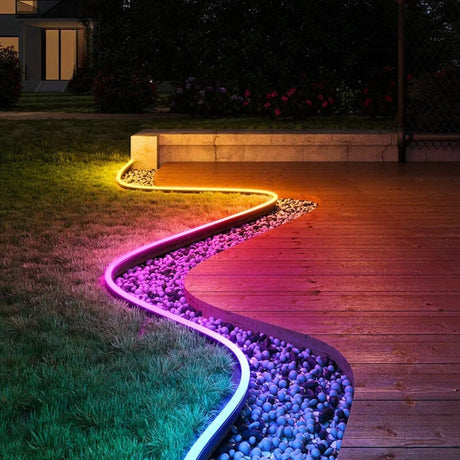
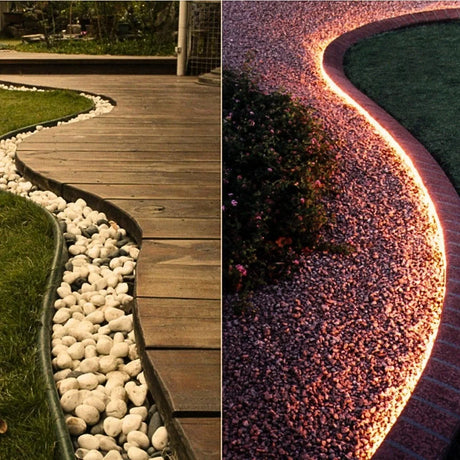
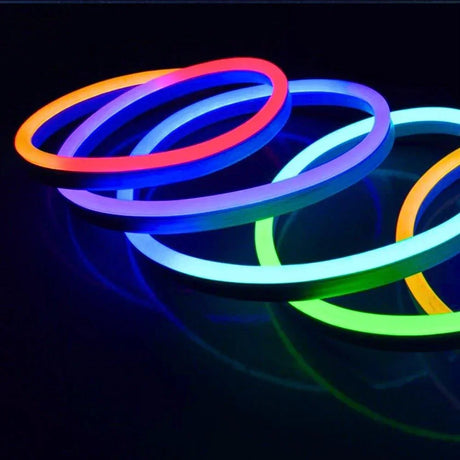
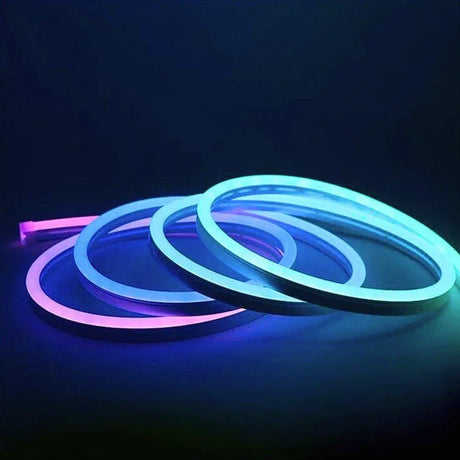
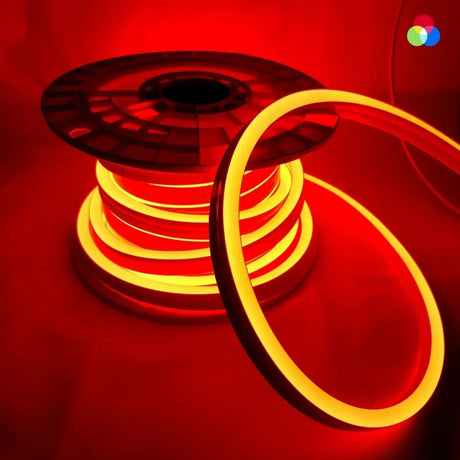
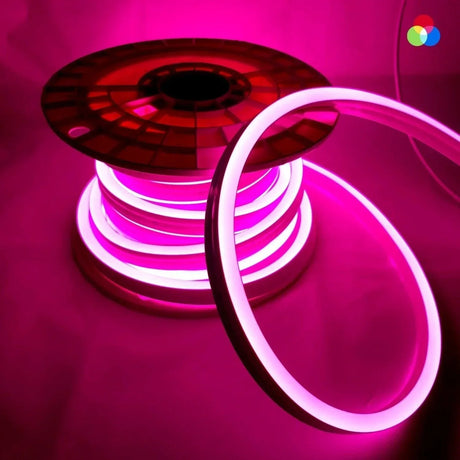
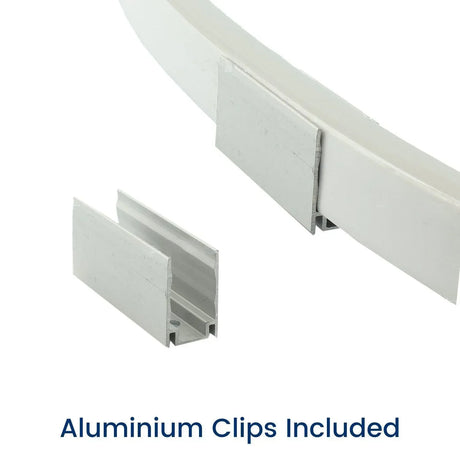
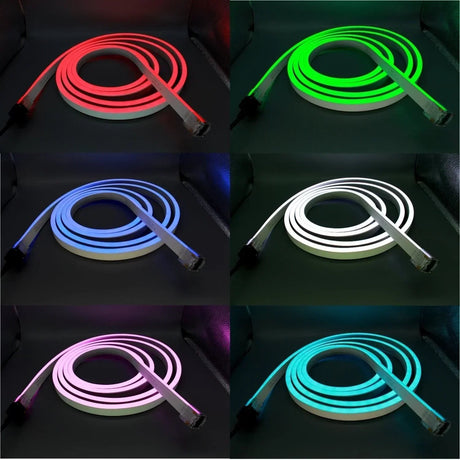
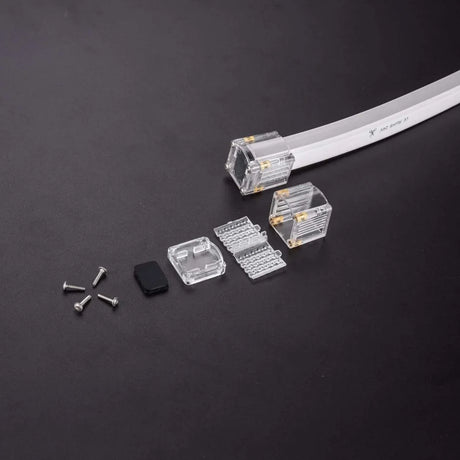
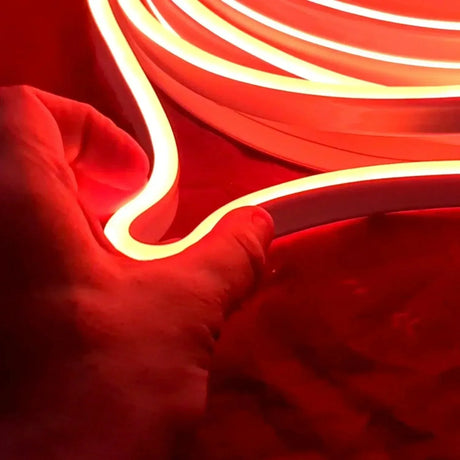
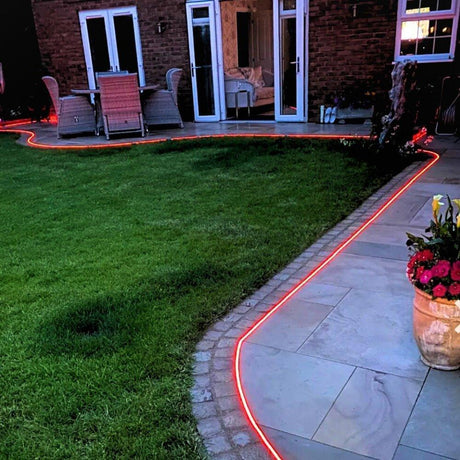
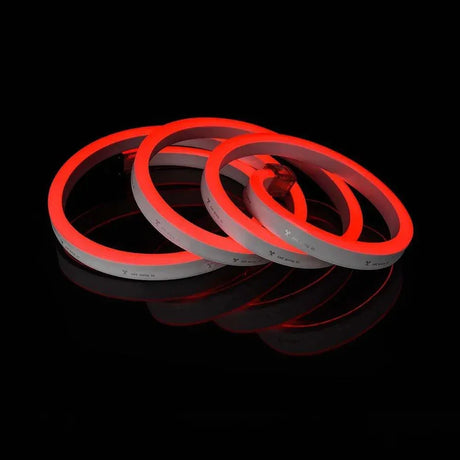
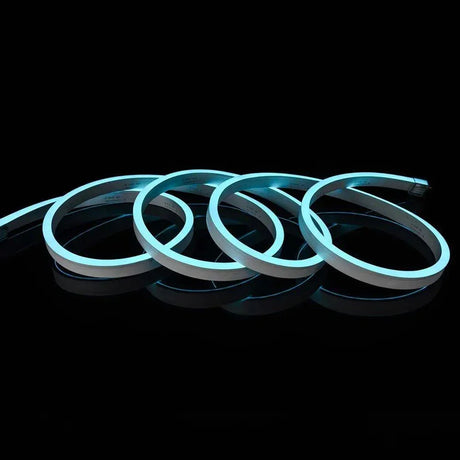
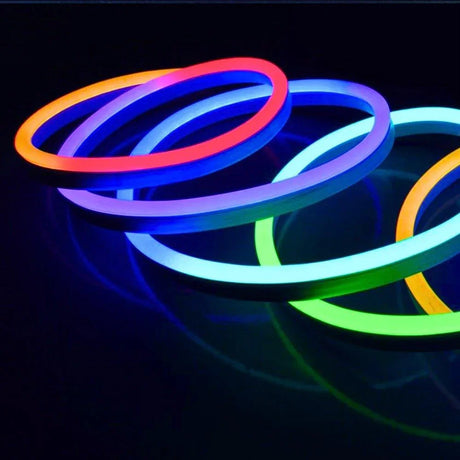
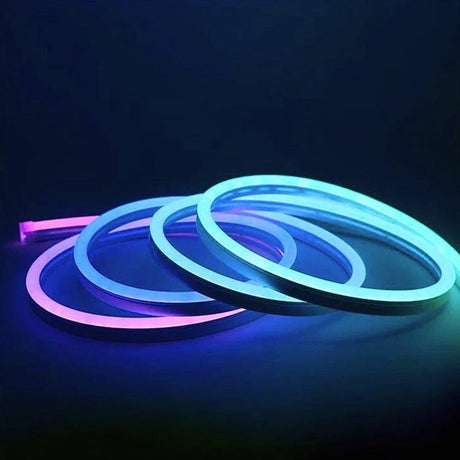
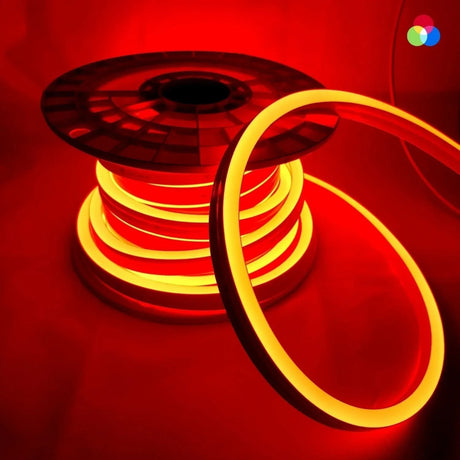
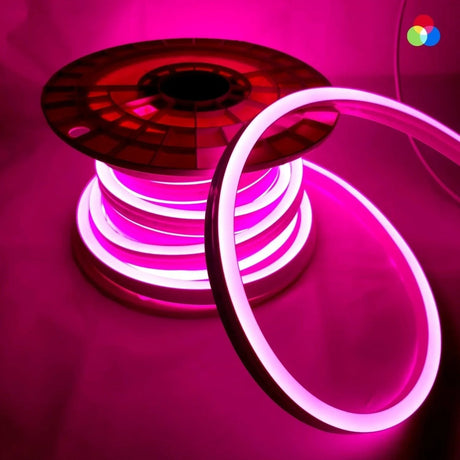
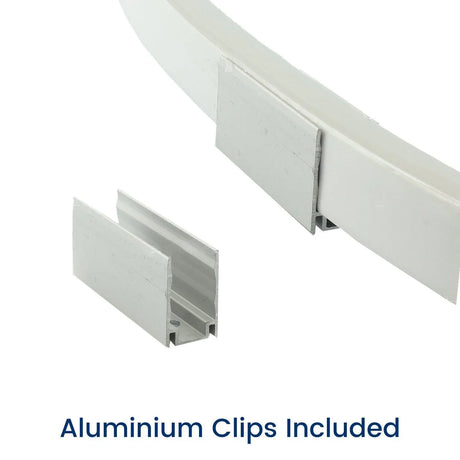
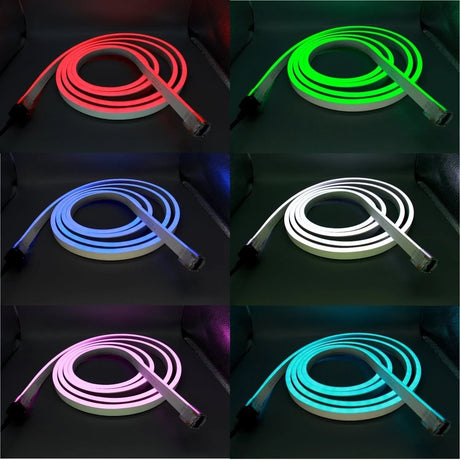
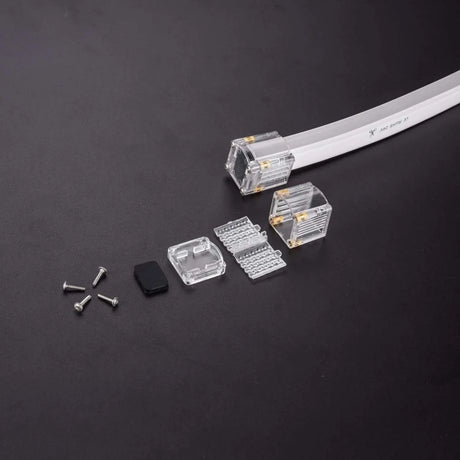
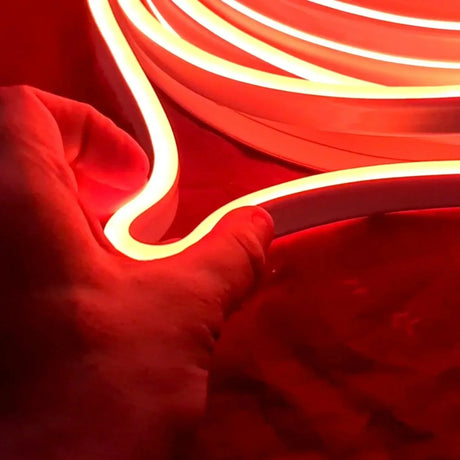
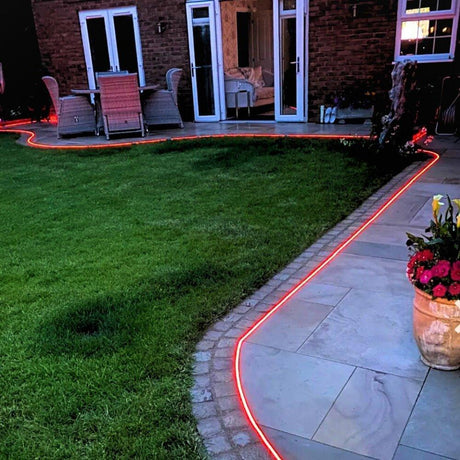
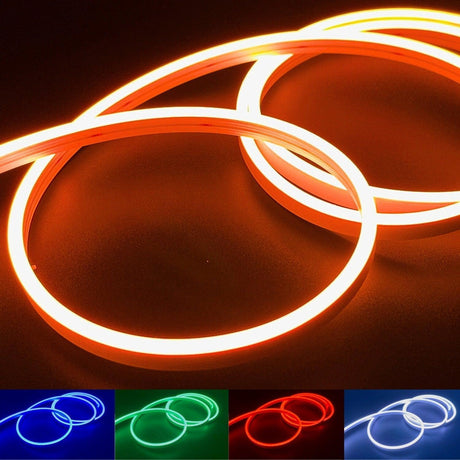
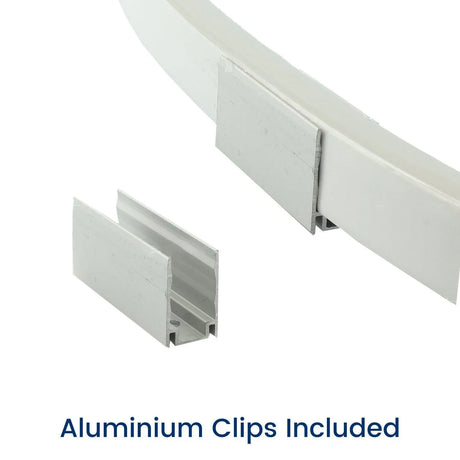
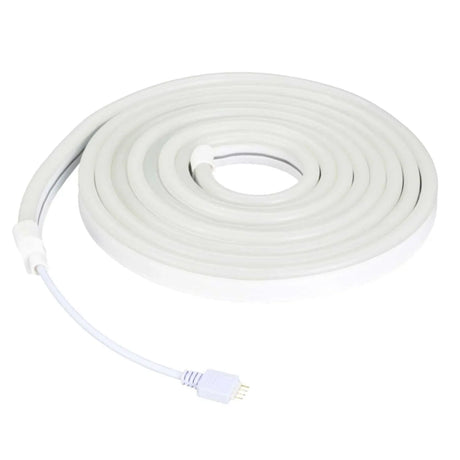
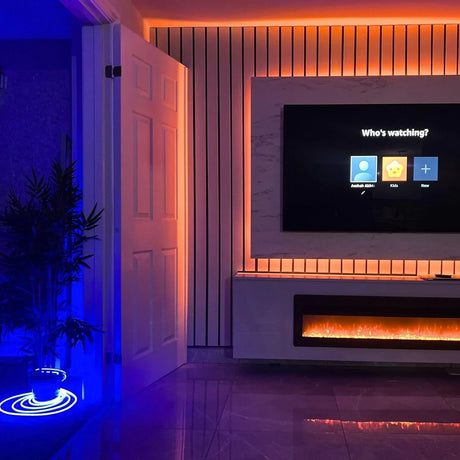
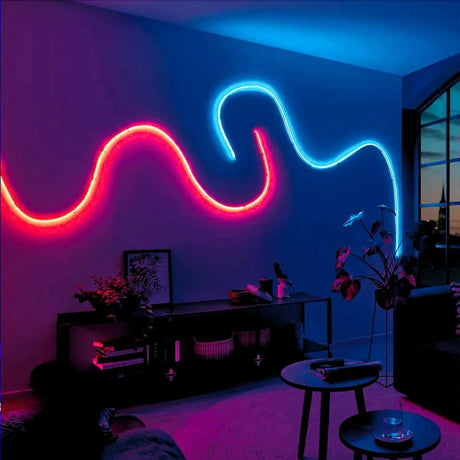
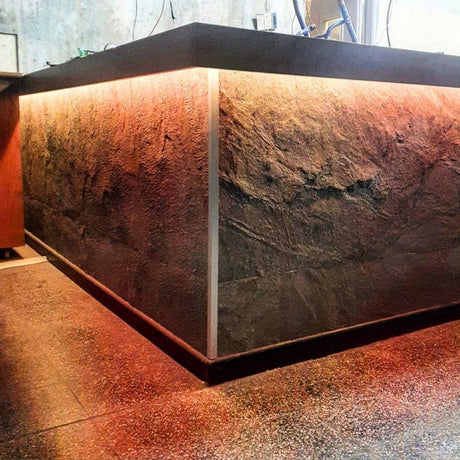
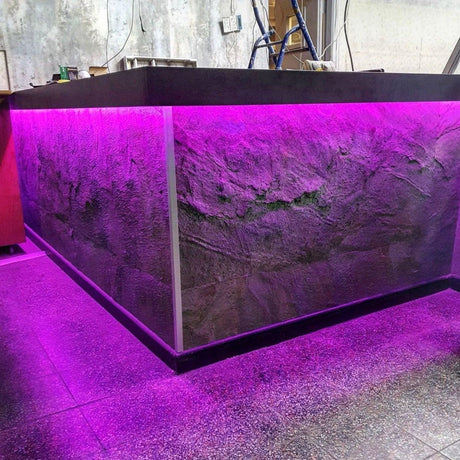
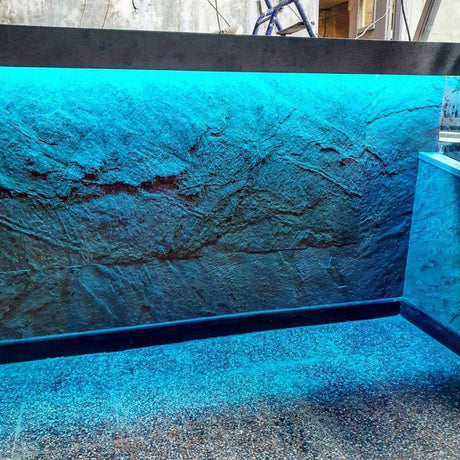
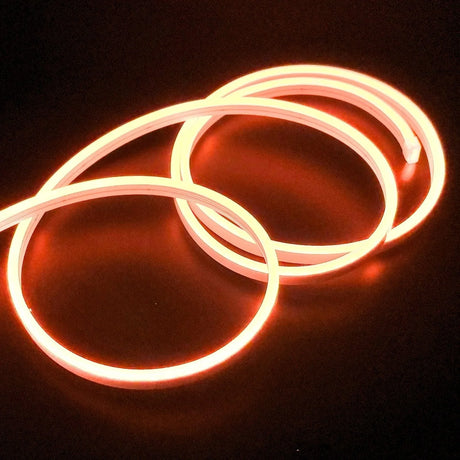
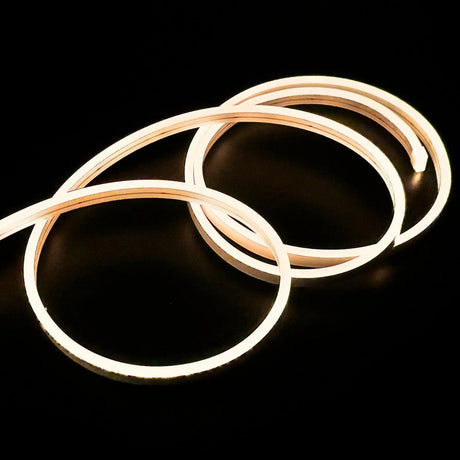
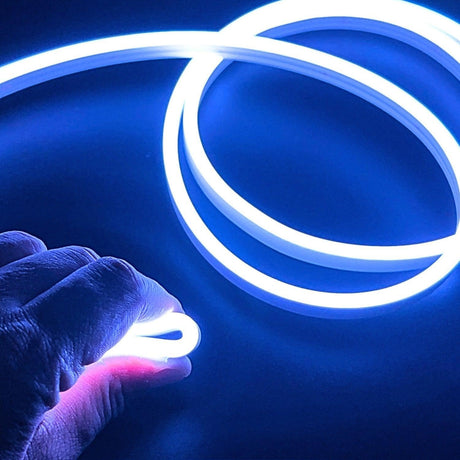
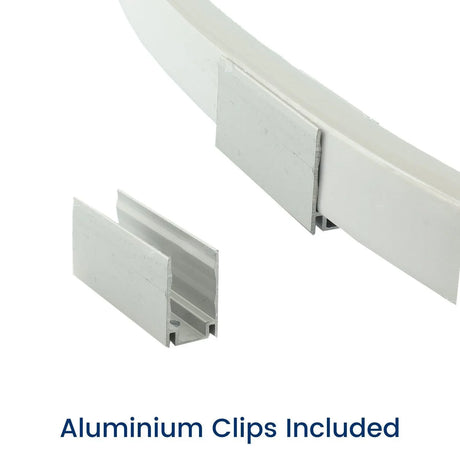
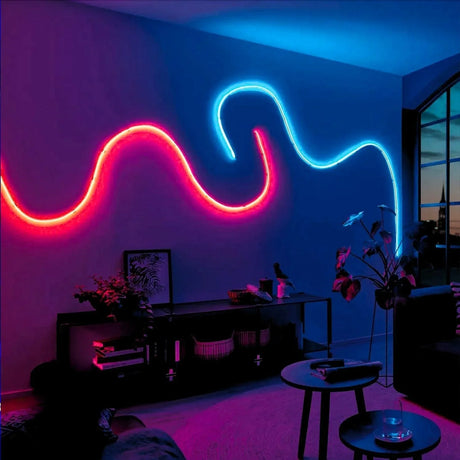
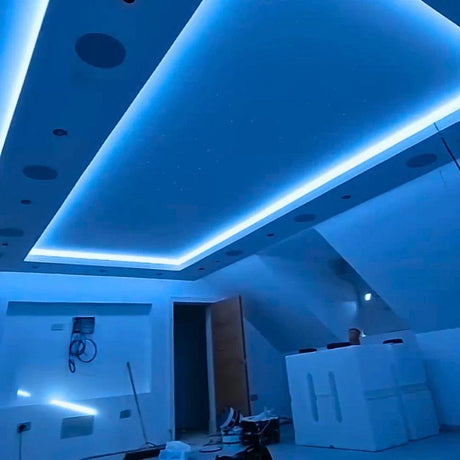
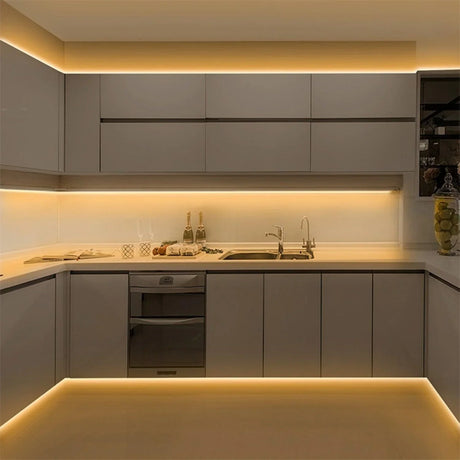
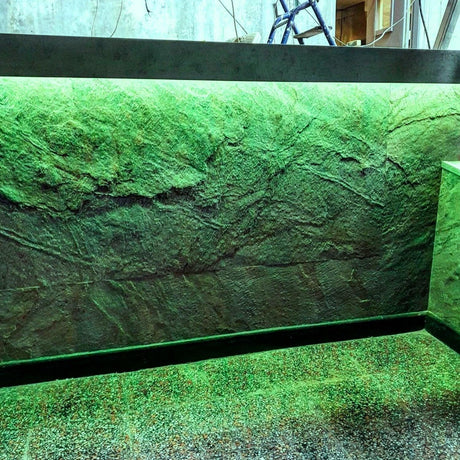
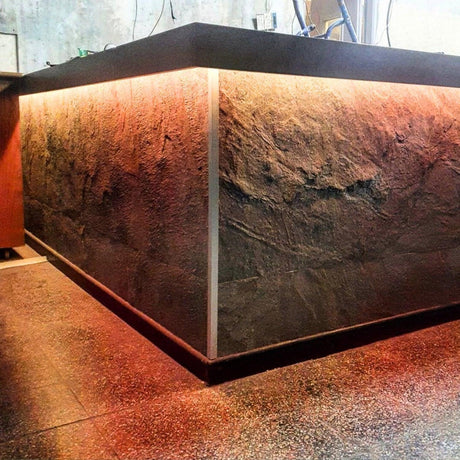
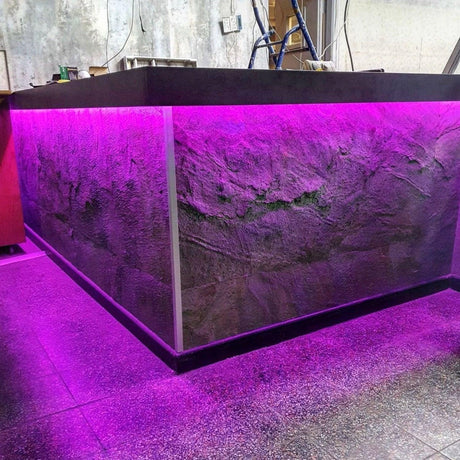
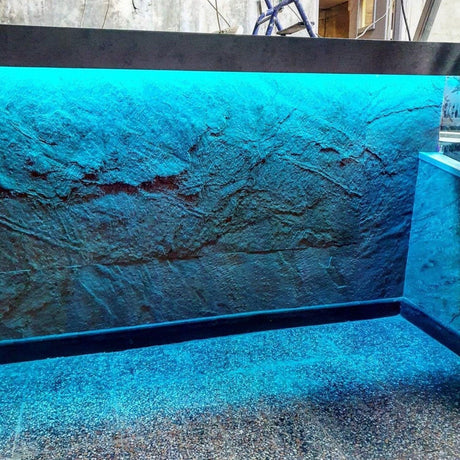
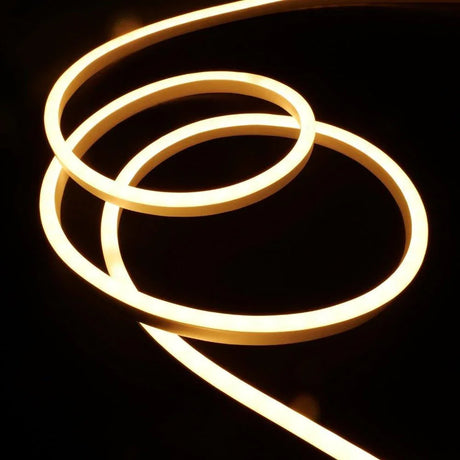
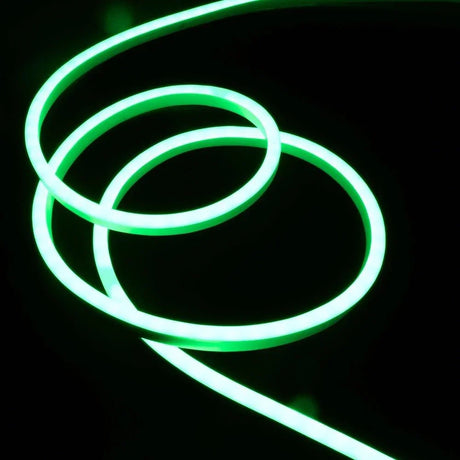
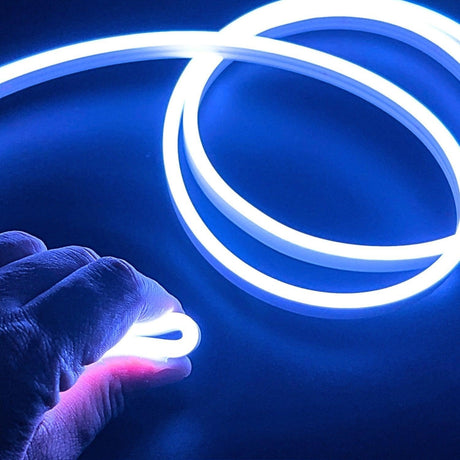
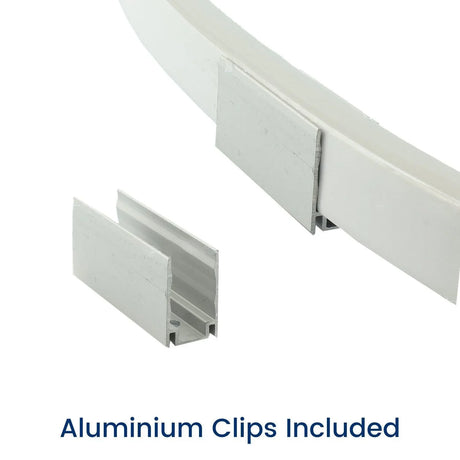
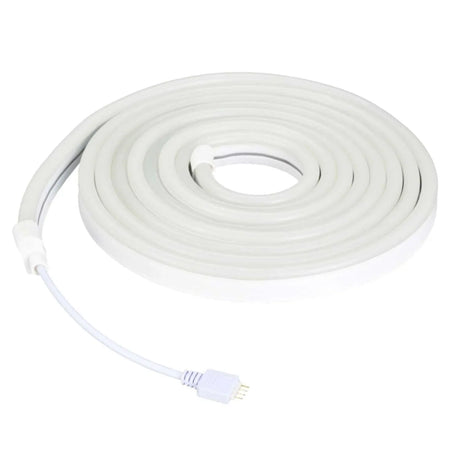
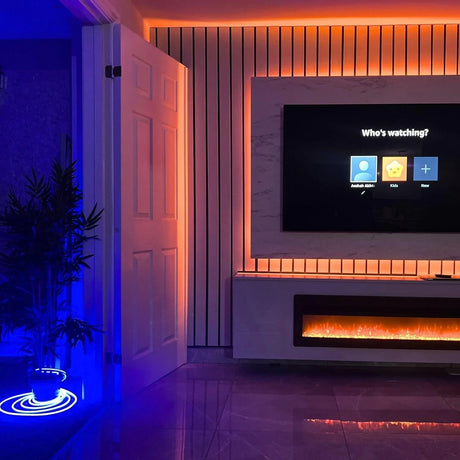
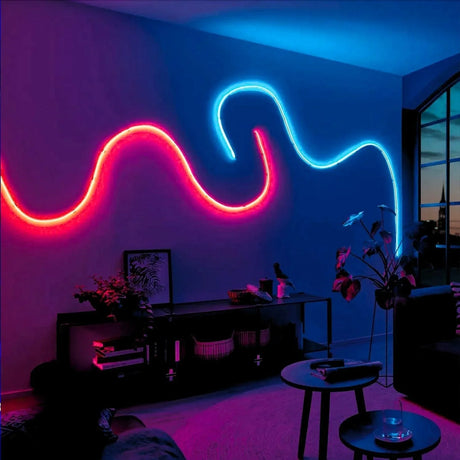
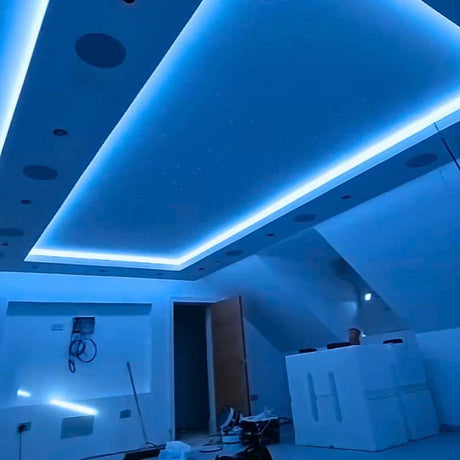
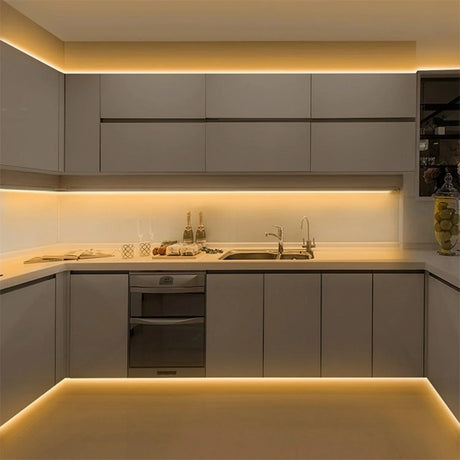
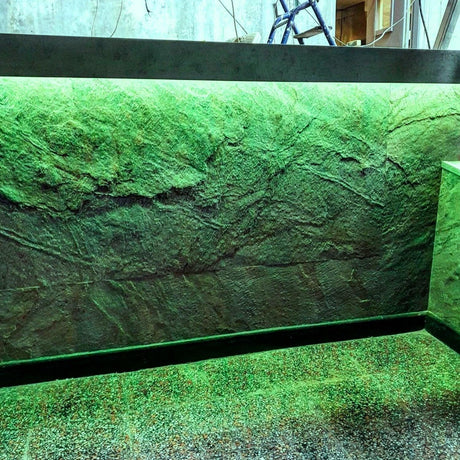
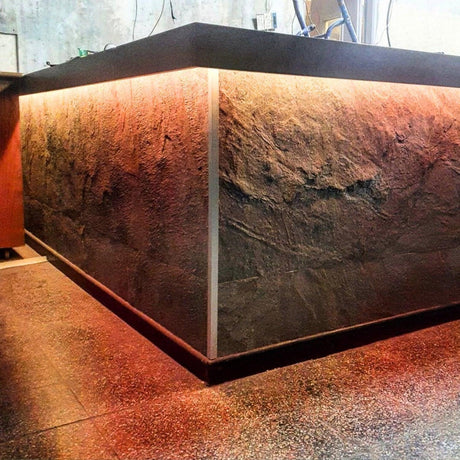
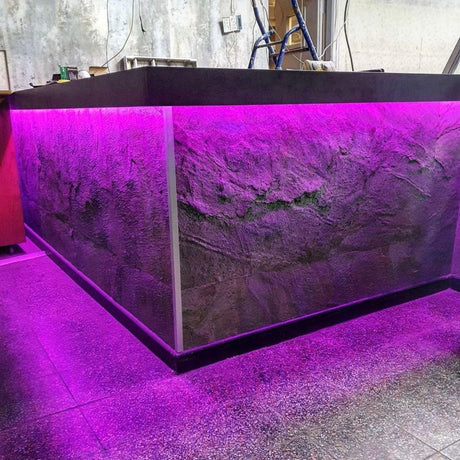
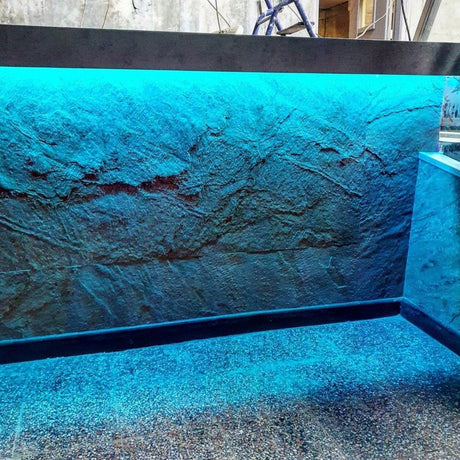
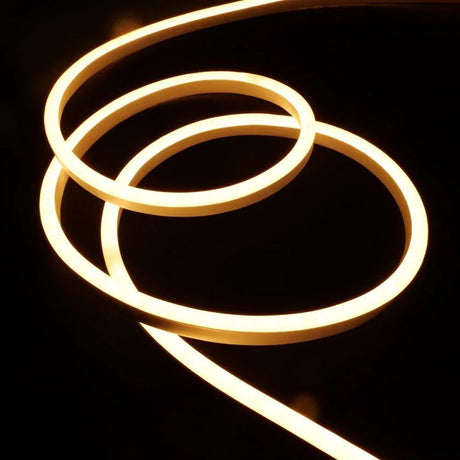
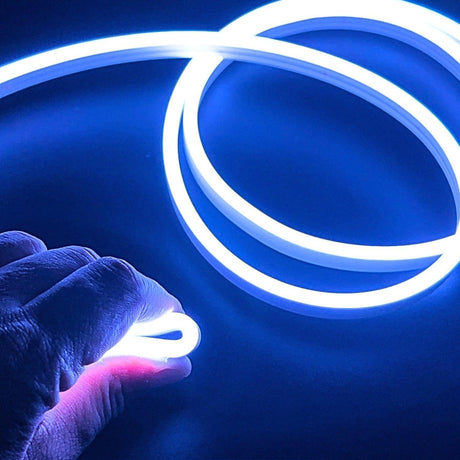
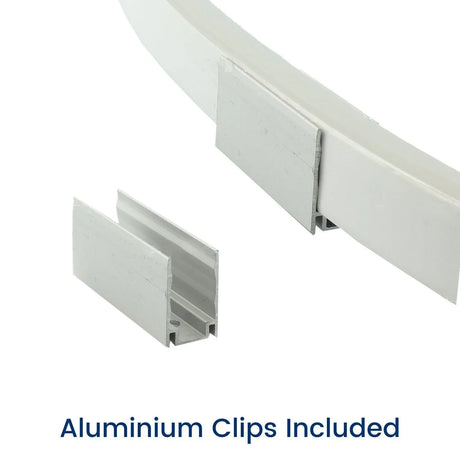
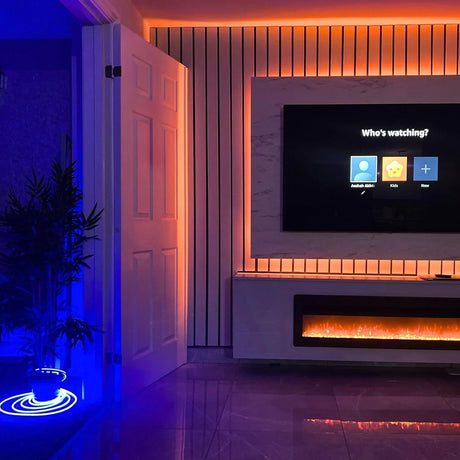
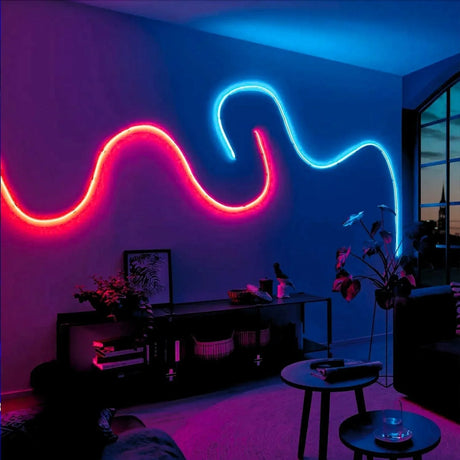
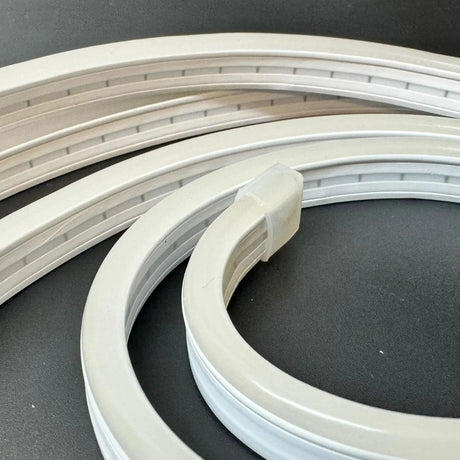
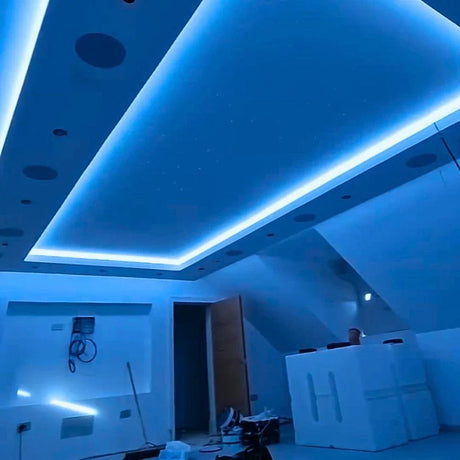
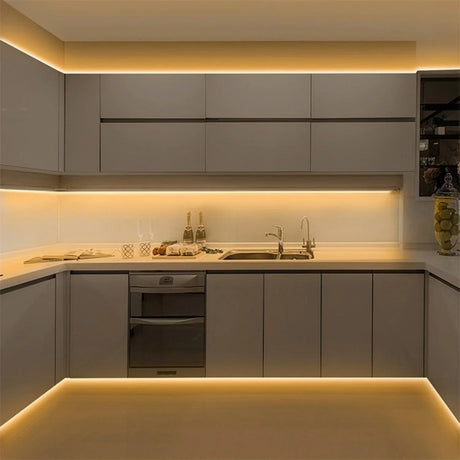
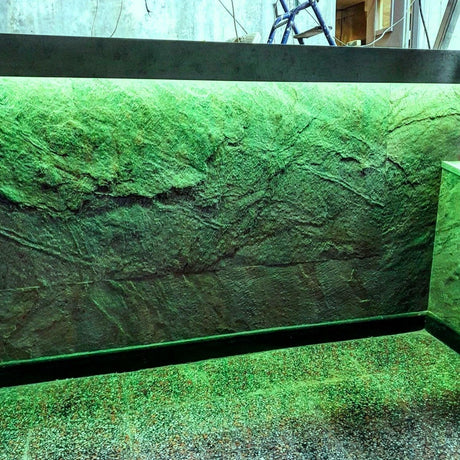
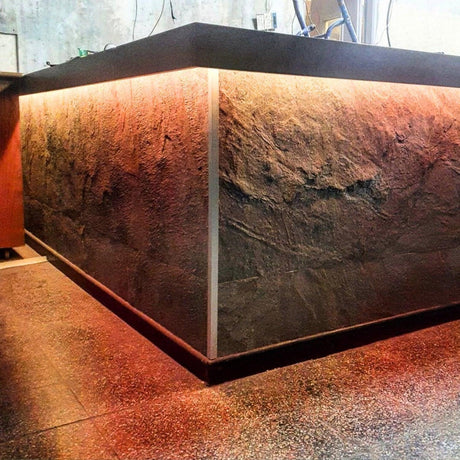
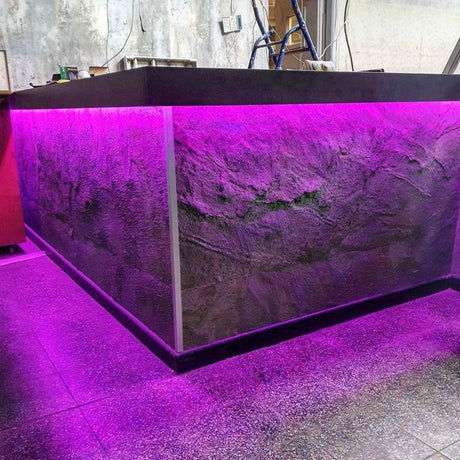
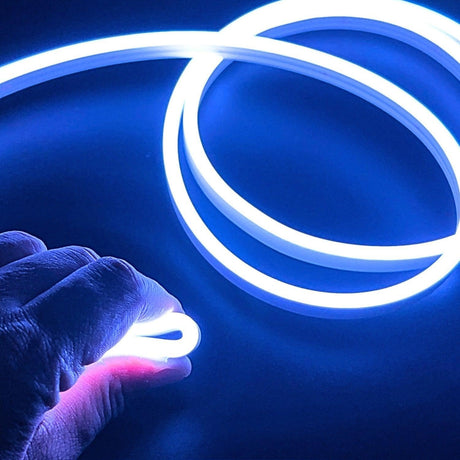
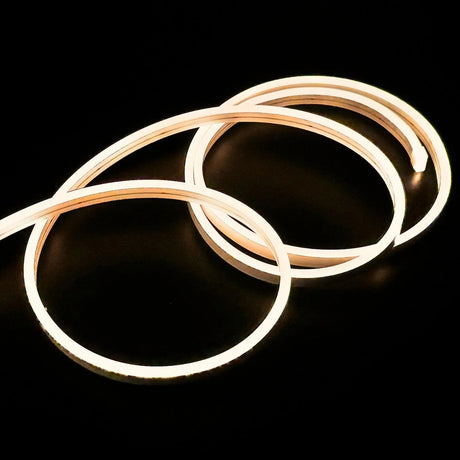
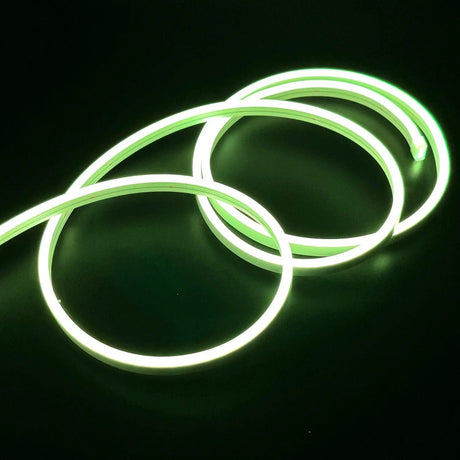
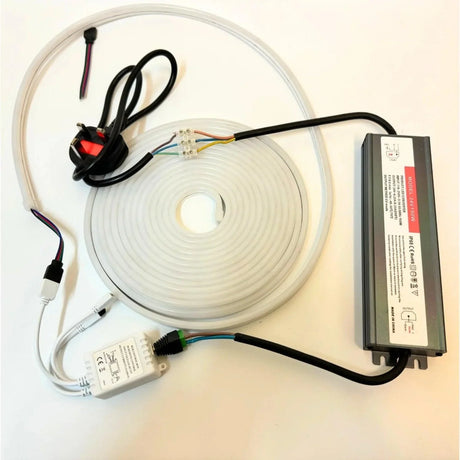
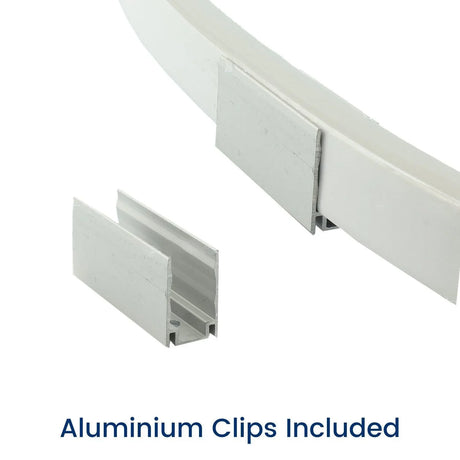
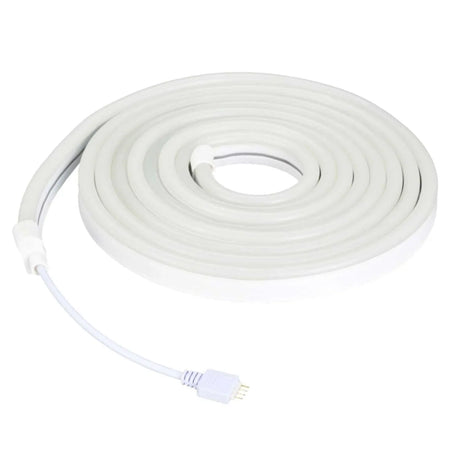
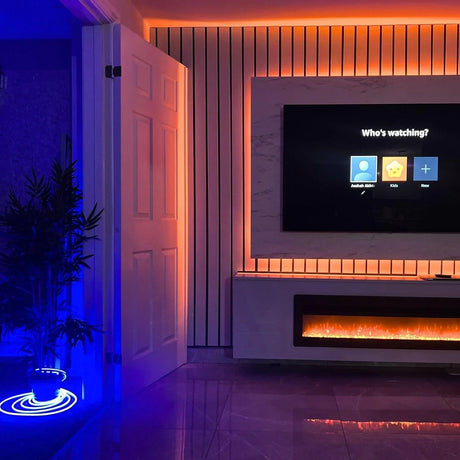
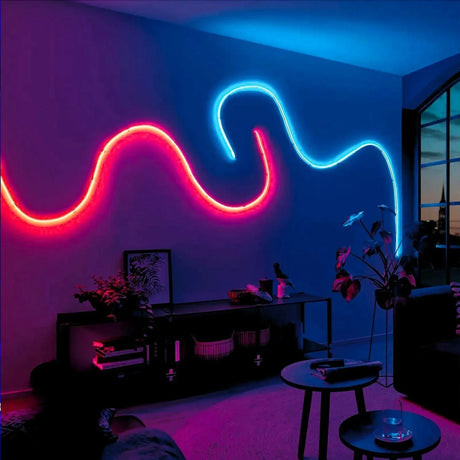
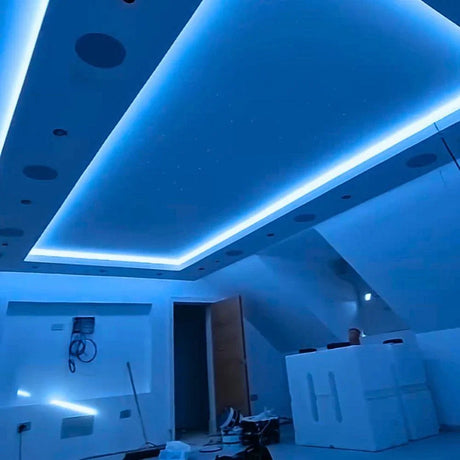
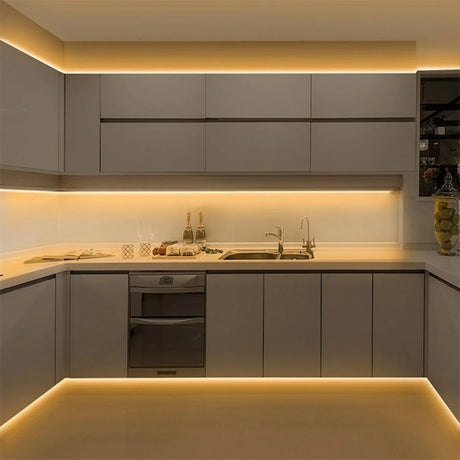
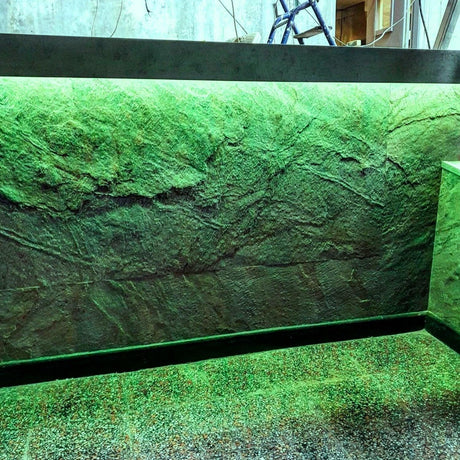
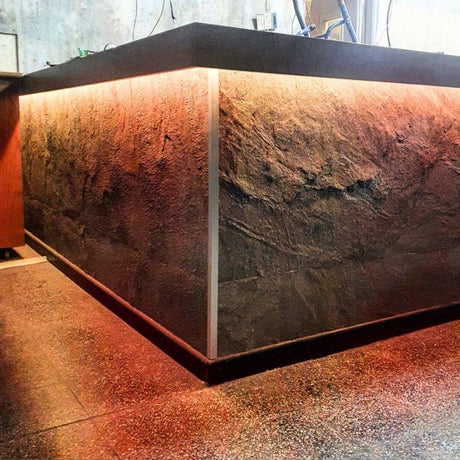
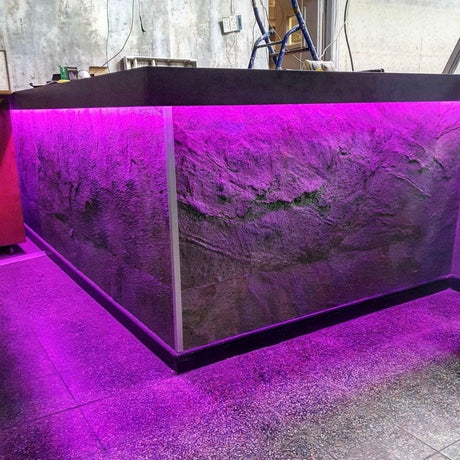
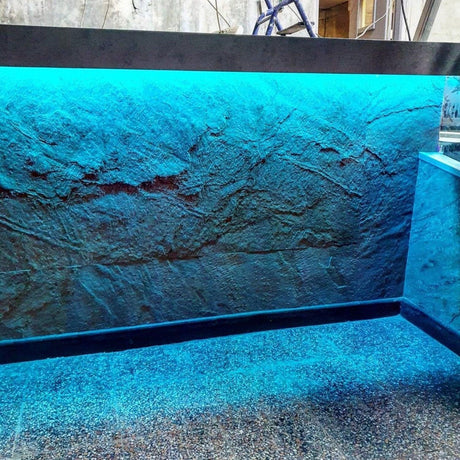
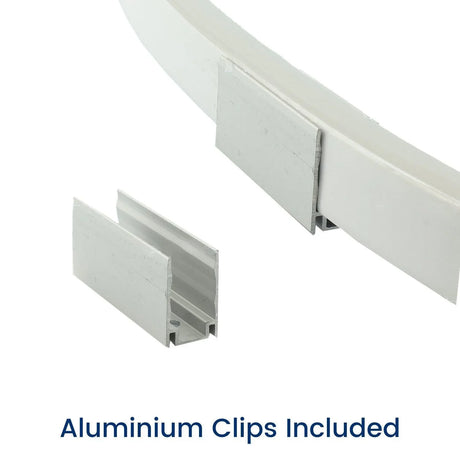
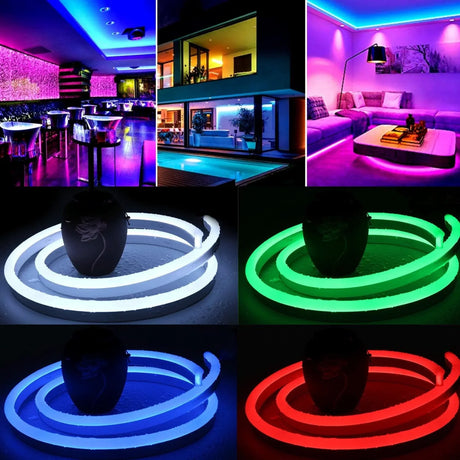
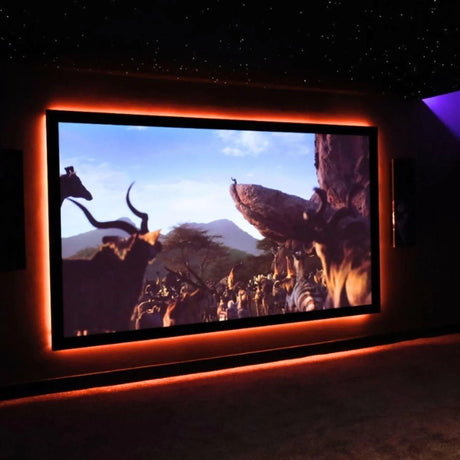
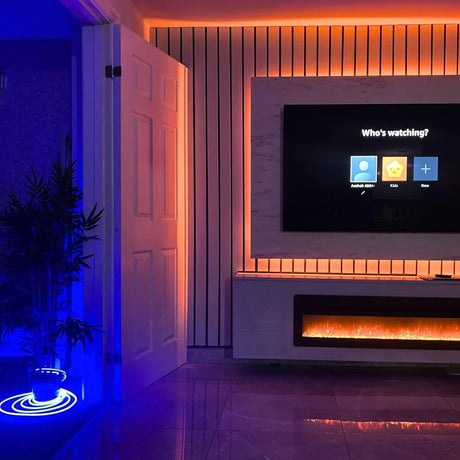
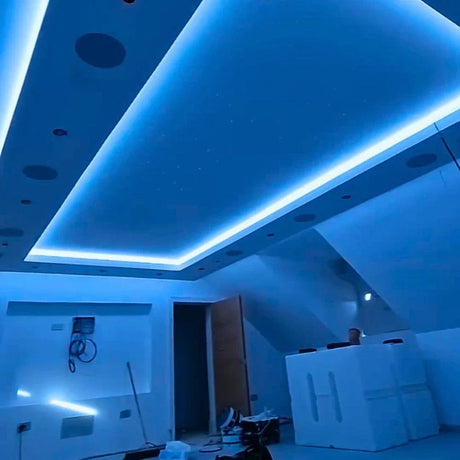
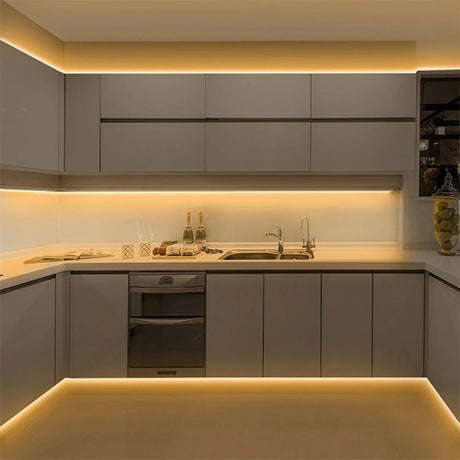
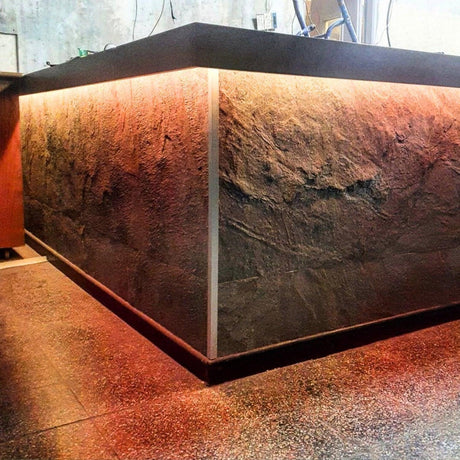
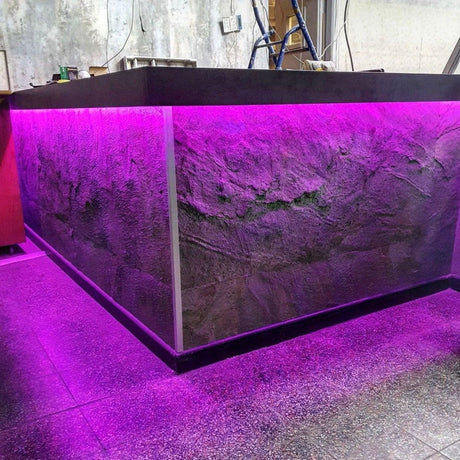
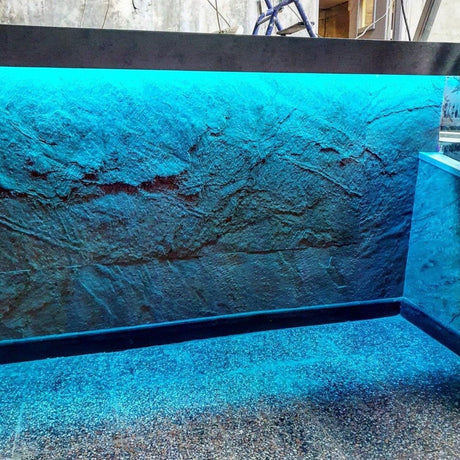
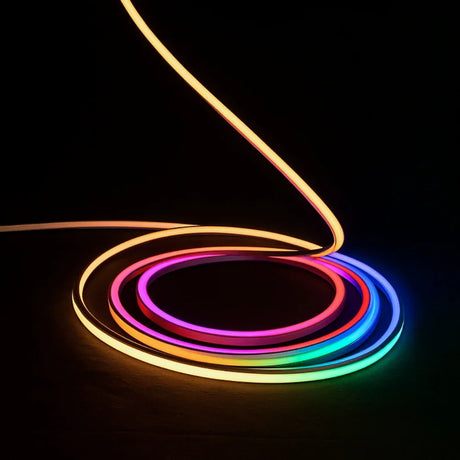
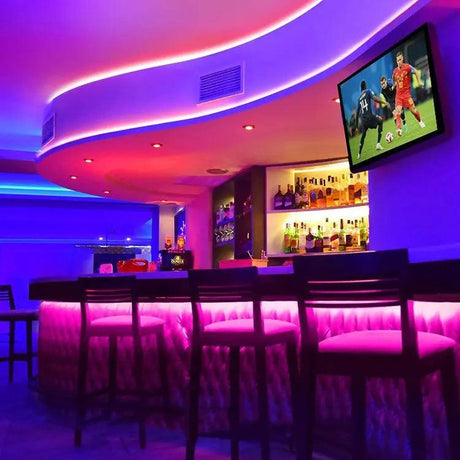
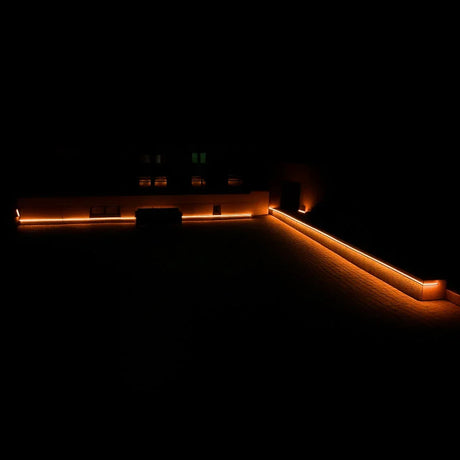
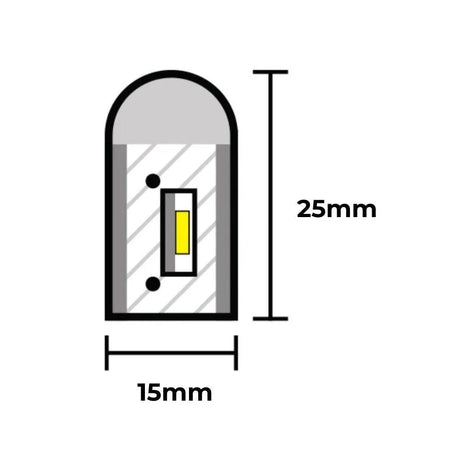
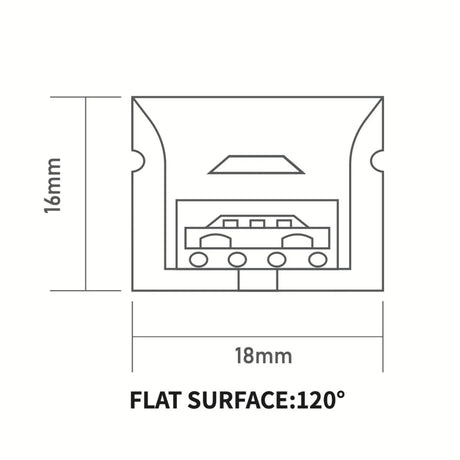
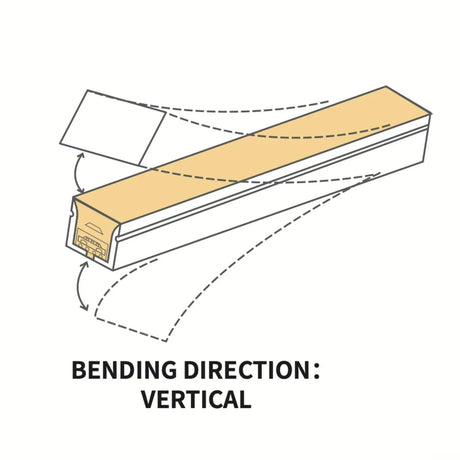
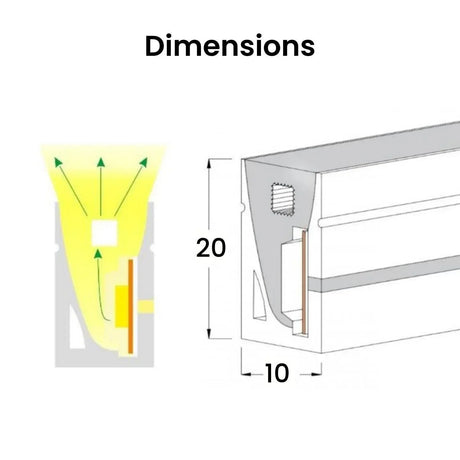
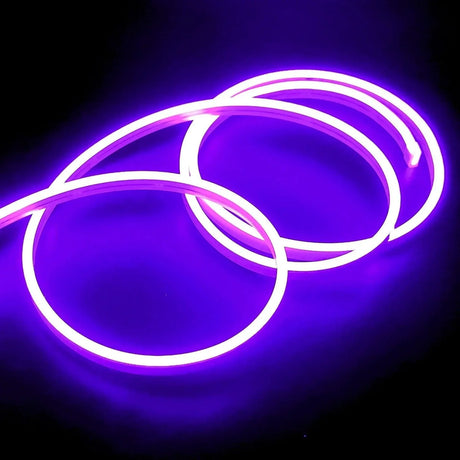
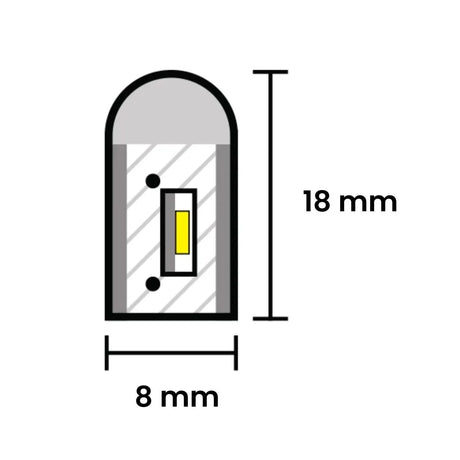
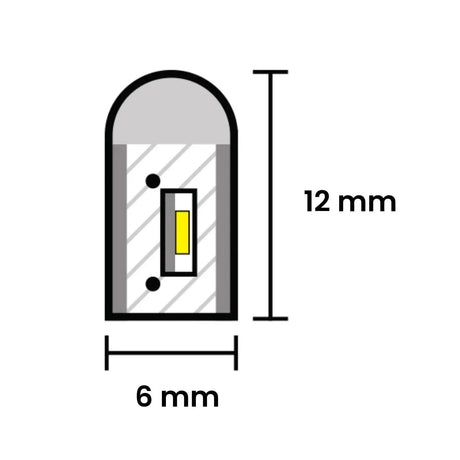
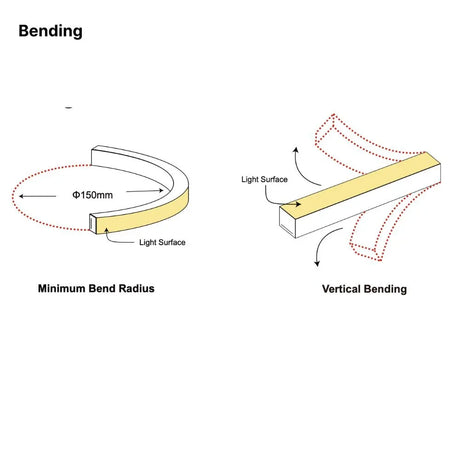
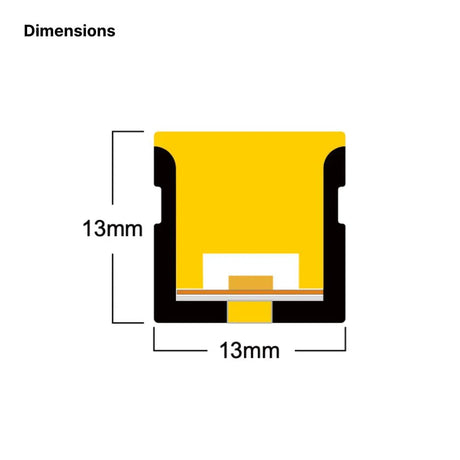
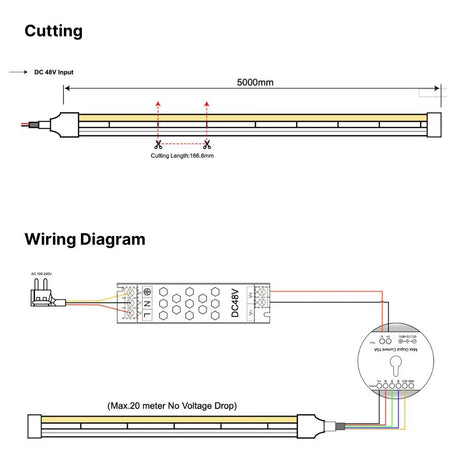
Ultra Long 18x16mm RGB Neon Flex 48V IP68 Top Bend Waterproof 30 Metre
From £44.50Unit price /UnavailableDigital Pixel RGB Neon Flex Addressable 24V 10x20mm IP68 Waterproof WS2811
From £39.95Unit price /UnavailableDigital Pixel RGB Neon Flex 24V Addressable 16x16mm IP65 Waterproof WS2811
From £27.85Unit price /UnavailableAddressable Digital Pixel RGB Neon Flex 24V 12x20 WS2811 IP65 Waterproof
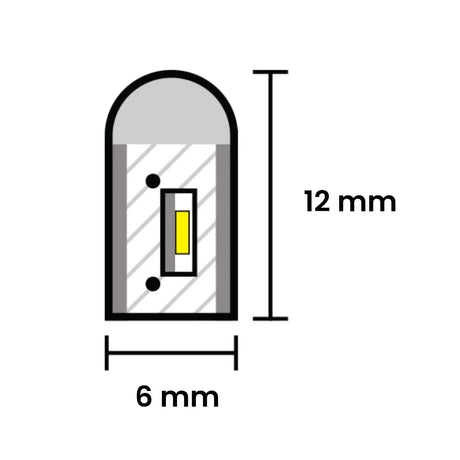
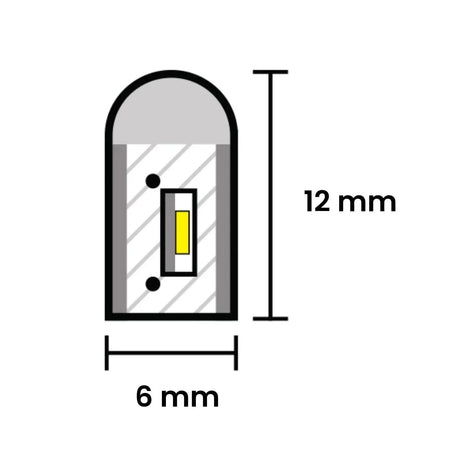
From £25.85Unit price /UnavailableMini RGB Neon Flex 6x12mm 12V IP65 Waterproof 5cm Cut
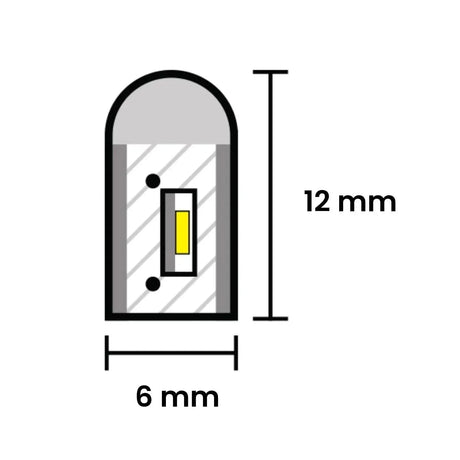
From £13.85Unit price /UnavailableRGB Neon Flex 6x12mm 24V IP65 Waterproof 5cm cut 10 Metre
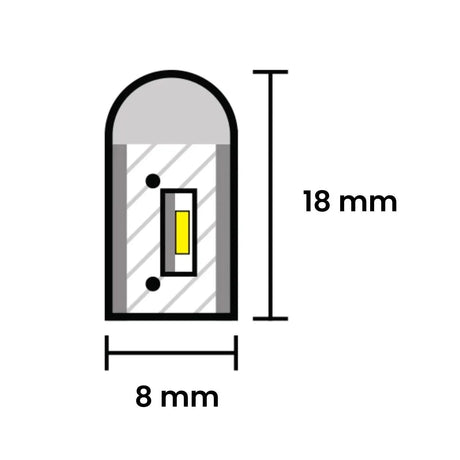
From £13.85Unit price /UnavailableRGB Neon Flex 8x18mm 24V IP65 Waterproof 10cm cut 10 Metre
From £13.85Unit price /UnavailableAddressable Digital Pixel RGB Neon Flex 24V 12x20mm IP65 WS2811 10cm Cut
From £25.85Unit price /UnavailableAddressable Digital Pixel RGB Neon Flex 16x16mm WS2811 App Control 10 metre Kit
From £75.85Unit price /UnavailableMini RGB Neon Flex 6x12mm 12V IP65 Waterproof 5cm cut 5m Kit
From £27.85Unit price /UnavailableMini RGB Neon Flex 6x12mm 24V IP65 Waterproof 5cm cut 10 Metre Kit
From £27.85Unit price /UnavailableRGBW (3000K) LED Neon Flex 13x13mm IP67 Waterproof 48V 20 Metre
From £21.95Unit price /Unavailable
What are the key differences between RGB Neon Flex 12V, 24V, and 48V in terms of run length, brightness, and efficiency?
Higher voltages allow longer continuous runs with less voltage drop, so 48V supports the longest distances, while 12V offers the most flexibility but shortest run lengths. Brightness consistency and efficiency improve as voltage increases.
When should installers choose 12V RGB Neon Flex instead of 24V or 48V for a project?
12V RGB Neon Flex is best for short runs, tight bends, furniture, vehicles, or DIY projects where safety, flexibility, and low-voltage operation are priorities.
How does voltage affect voltage drop and color consistency along long runs of RGB Neon Flex?
Lower-voltage systems experience voltage drop sooner, which can cause dimming or color shift at the far end, while 24V and 48V maintain more uniform brightness and color over longer distances.
How do driver and cable sizing differ for 12V, 24V, and 48V RGB Neon Flex installations?
Lower voltages require thicker cables and more frequent power injection, whereas higher voltages allow thinner cables and fewer injection points due to reduced current draw.
What is the maximum recommended run length for each voltage (12V, 24V, 48V) before extra feeds or power injection are needed?
Typical limits are around 5 m for 12V, 10 m for 24V, and 20 m or more for 48V, depending on wattage per metre and installation conditions.
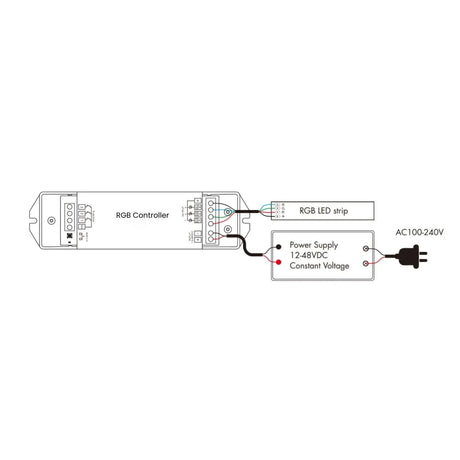
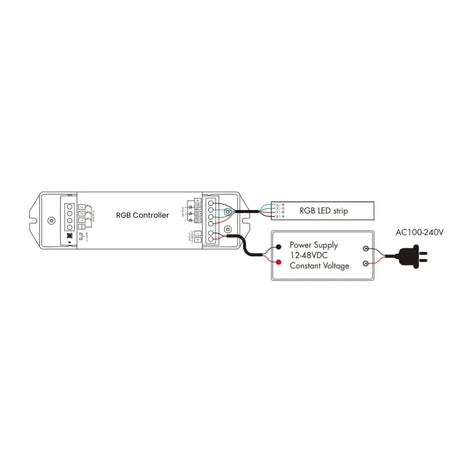
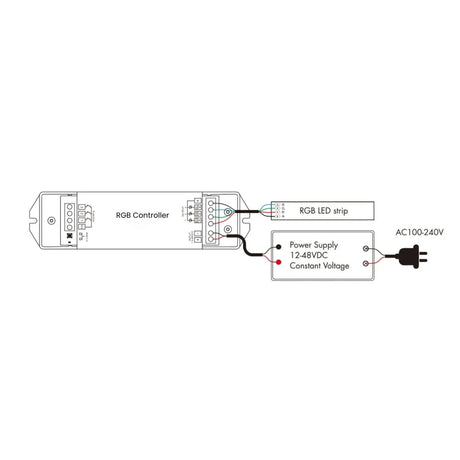
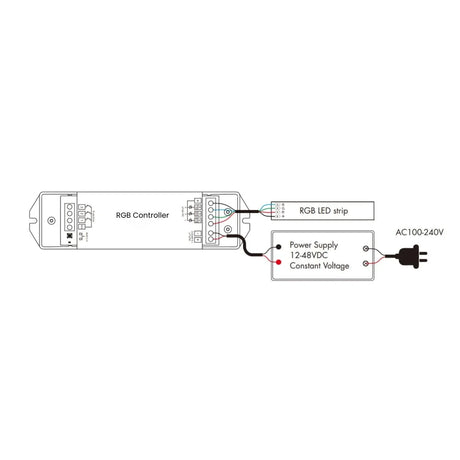
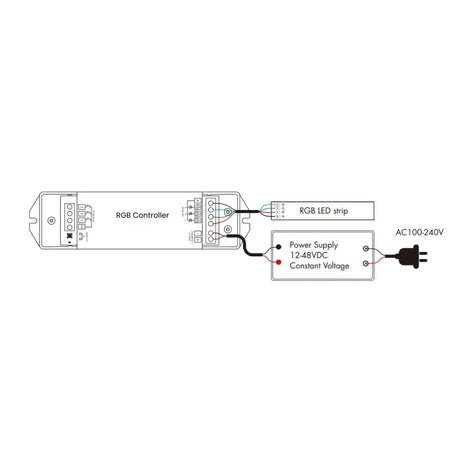
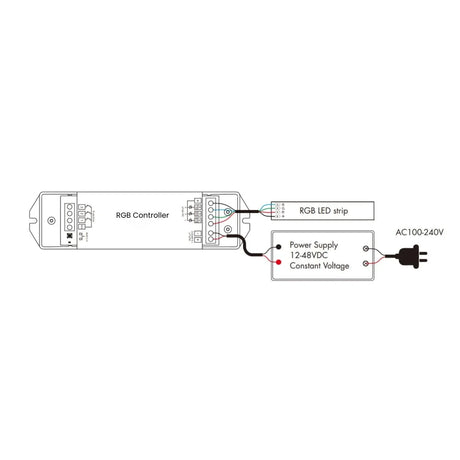
How should RGB Neon Flex 12V/24V be wired to controllers and amplifiers to maintain even colour and brightness?
Power should be injected evenly along the run, with signal amplifiers used on longer lengths to maintain consistent RGB control and avoid colour imbalance.
Why are 12V and 24V RGB Neon Flex considered safer for domestic and DIY projects than mains-voltage 220–240V kits?
Low-voltage systems significantly reduce electric shock risk and typically do not require certified electricians, making them safer and more accessible for home installations.
In what situations might 48V RGB Neon Flex be preferable from a safety and design perspective over high-voltage neon flex solutions?
48V offers long-run capability similar to mains systems while remaining extra-low voltage, balancing improved safety with professional-grade performance.
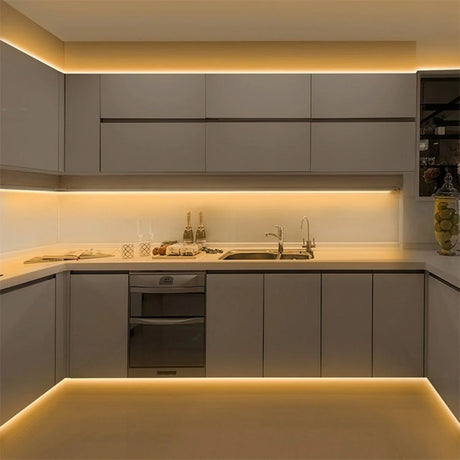
Which applications are best suited to 12V RGB Neon Flex (for example, camper vans, furniture, signage) versus 24V and 48V systems?
12V suits compact and mobile installs, 24V works well for residential architectural lighting, and 48V is ideal for large commercial outlines and long linear runs.
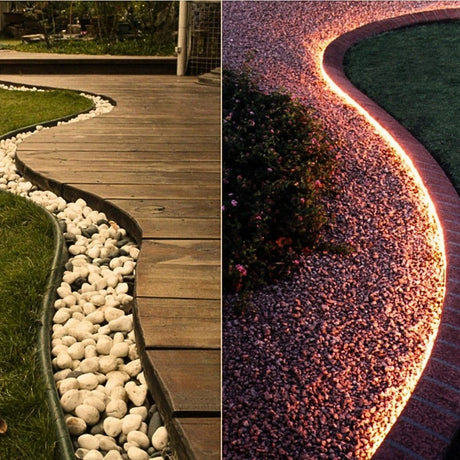
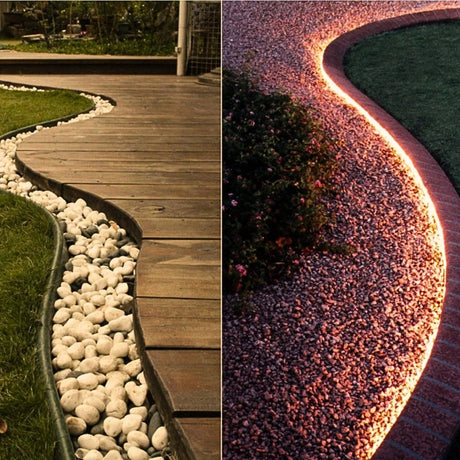
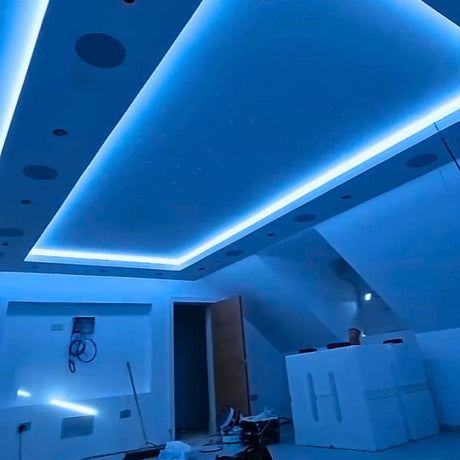
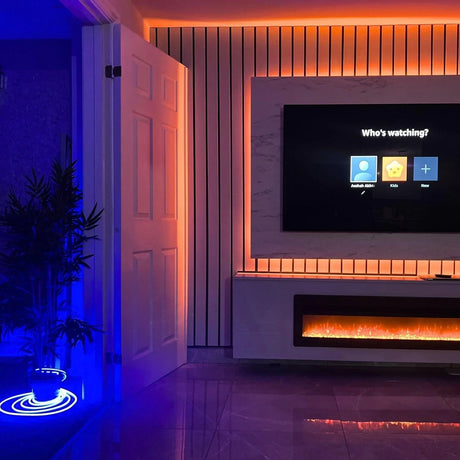
How can 24V RGB Neon Flex be used effectively for garden, decking, and cove lighting in UK homes and hospitality spaces?
It provides stable brightness over moderate distances, works well with weatherproof controllers, and integrates neatly into aluminium channels for clean outdoor and indoor accents.
Where does 48V RGB Neon Flex shine in commercial projects such as long building outlines or industrial façades?
48V excels in large-scale installations where long continuous runs, minimal power injection, and consistent illumination are required.
What should buyers compare when choosing between RGB Neon Flex 12V, 24V, and 48V (IP rating, lumen output, run length, bend radius)?
Key factors include environment (IP rating), required brightness, maximum continuous run length, minimum bend radius, and controller compatibility.
How do UK suppliers like UK LED Lights and Atom LED position their 12V, 24V, and 48V RGB Neon Flex ranges for different customer types?
Ranges are typically segmented by voltage to suit DIY users, residential installers, and commercial professionals, with higher voltages aimed at large-scale or trade projects.